Severe COVID-19 Fallout Evident in Airbus, Boeing Q2 Earnings Reports
by J. Kasper Oestergaard, European Correspondent, Forecast International.

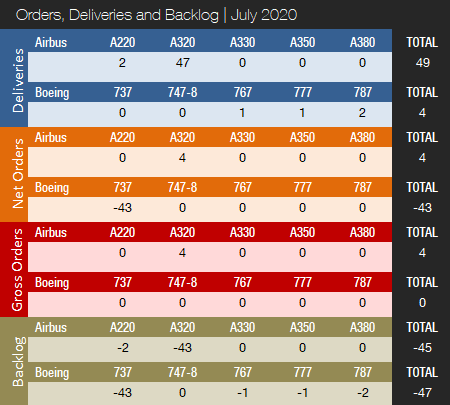
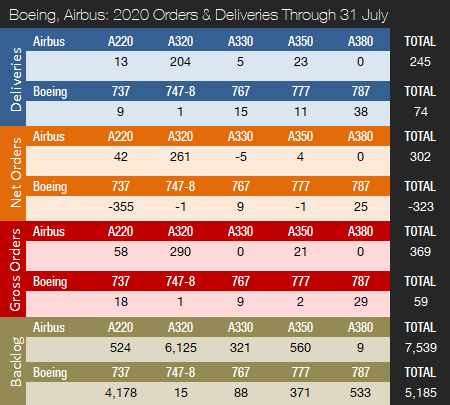
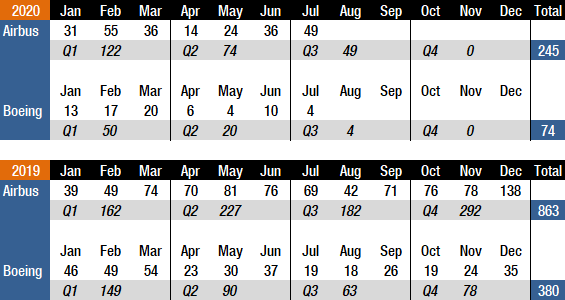
Boeing and Airbus delivered 4 and 49 commercial jets in July 2020, compared to 19 and 69 deliveries, respectively, in the same month last year. With just 74 deliveries this year to date, Boeing is 184 shipments behind last year’s total for the seven months of the year. Airbus delivered a total of 245 jets from January to July, compared to 458 during the same period last year. Boeing’s deliveries have suffered for many months in the aftermath of two 737 MAX crashes and the subsequent suspension of deliveries and grounding of the fleet. Deliveries of 737 MAX aircraft have been on hold since March 2019. Due to COVID-19, both manufacturers were forced to temporarily close down production facilities and have also laid off thousands of employees and announced significant production rate cuts. For the full year 2019, Boeing delivered 380 aircraft, while Airbus set a new all-time annual record, handing over 863 jets. Prior to this, Boeing had retained a deliveries lead over Airbus since 2012. In 2018, Boeing delivered 806 jets (763 in 2017), with Airbus handing over 800 (718 in 2017).
In July, Boeing delivered just four aircraft, including one 767-300F, one 777F, and two 787-9s. Production of the 737 MAX was suspended from January this year until the end of May. On May 27, Boeing announced it had resumed production of the 737 MAX in Renton. Aircraft are being built at a low rate. Boeing expects the 737 MAX production rate to gradually increase to 31 per month by the beginning of 2022, with further increases as market demand allows. Boeing has also announced that the 787 production rate is being reduced from 14 per month (the rate at the start of the year) to just six per month during 2021. The combined 777/777X production rate will be reduced to two per month in 2021. Production rate assumptions have not changed for the 747 and 767 programs. Prior to the recent 737 MAX production suspension, Boeing was manufacturing the jet at a reduced rate of 42 per month. While the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has repeatedly stated that it has no timetable for the aircraft’s return to service, the 737 MAX is expected to remain grounded until fall. Boeing currently hopes to get the 737 MAX flying again commercially by early 2021. In any case, it will be a few years before Boeing is able to hit the originally planned monthly production rate of 57 aircraft. Prior to the suspension of deliveries in March 2019, Boeing had produced and shipped 387 737 MAX jets. Between June 29 and July 1 this year, a number of 737 MAX certification flight tests were carried out by Boeing and the FAA to evaluate Boeing’s proposed changes to the automated flight control system. Following the flights, the FAA announced that, while this was an important milestone, a number of key tasks remain. These include a number of evaluation reviews and reports held and issued by the FAA and the Joint Operations Evaluation Board (JOEB), which includes international partners from Canada, Europe, and Brazil. Next, a Continued Airworthiness Notification to the International Community (CANIC) and an Airworthiness Directive (AD) will be issued, followed by the official ungrounding of the aircraft. On August 3, a key milestone was reached when the FAA released a 36-page document in which it proposes a new AD that will allow the aircraft to return to service. The document lists four design changes, including the installation of new flight control computer software, revising the existing flight manual to incorporate new and revised flight crew procedures, installing new display system software, and changing the horizontal stabilizer trim wire routing installations. The FAA’s review of the 737 MAX has involved 40 engineers, inspectors, pilots, and technical support staff who logged more than 60,000 hours of review, certification testing, and evaluation. The FAA says it analyzed more than 4,000 hours of Boeing’s flight and simulator tests and did 50 hours of its own testing.
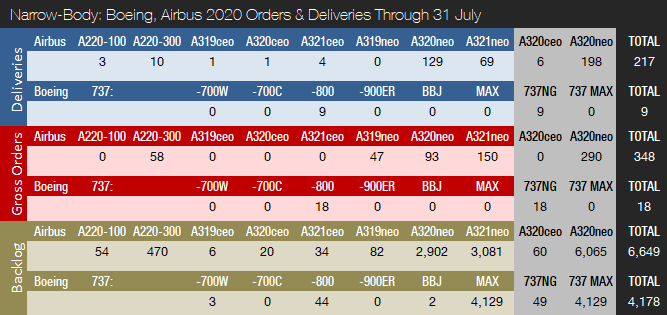
In July, Airbus delivered two A220s and 47 A320s (all NEO). No widebody aircraft were delivered. Prior to COVID-19, Airbus was targeting a 5 percent A320 rate increase to 63 jets per month from 2021, and was also discussing a further ramp-up with its supply chain that could have brought the production rate up as high as 67 aircraft per month, or 804 per year, by 2023. This would have put the company within reach of a total of 1,000 jets deliveries per year. These plans have now been shelved. For the full year 2019, Airbus handed over 642 A320 family aircraft, of which 551 were NEOs, while also delivering a record 112 A350s.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Airbus has cut production on several programs and is looking to hold underlying jet output at 40 percent below pre-pandemic plans for two years. The A320 production rate has been reduced to 40 aircraft per month, down from an average of over 53 aircraft per month in 2019. The A330 and A350 programs are reduced to a rate of two and six aircraft per month, respectively. No rate cut has been announced for the A220 or A380. On June 30, Airbus announced it plans to cut 14,000 jobs (5,000 in France, 5,100 in Germany, 900 in Spain, 1,700 in the U.K. and 1,300 elsewhere) as it deals with the effects of the coronavirus crisis. In the meantime, Boeing expects to reduce its global workforce by 10 percent, or 16,000 employees, this year. In the U.S., 12,300 jobs will be cut, including nearly 10,000 in Washington alone. Recently, Boeing carried out a second round of layoffs involving an additional 1,030 employees that will leave the company by the end of August. In connection with the release of the company’s second-quarter earnings on July 29, Boeing announced that further job cuts are being considered.
Turning to the orders race, in July, Boeing did not receive any new orders. However, the company reported 43 737 MAX cancellations. Year-to-date, Boeing has accumulated 59 gross orders (425 cancellations => -366 net new orders). For the full year 2019, Boeing booked 243 gross orders (330 cancellations => -87 net new orders). For the full year 2018, Boeing booked 893 net new orders and 1,008 gross orders.

In July, Airbus booked an order from an undisclosed customer for two A320neos and Lufthansa placed an order for two A321neos. For 2020 to date, Airbus has accumulated 369 gross orders (67 cancellations => net of 302). For the full year 2019, Airbus landed 1,131 gross orders (363 cancellations => net of 768), thereby retaking the orders crown from Boeing. In 2018, Airbus booked a total of 747 net new orders and 831 gross orders, thereby losing the 2018 orders race. Prior to this, Airbus had retained an orders lead over its rival every year since 2012.
At the end of July, Airbus’ reported a backlog of 7,539 jets, of which 6,649, or 88 percent, were A220 and A320ceo/neo family narrowbodies. This is 186 aircraft below the company’s all-time backlog record of 7,725 aircraft set in January 2020. By the end of July 2020, Boeing’s backlog (total unfilled orders before ASC 606 adjustment) was 5,185 aircraft, of which 4,178, or 81 percent, were 737 NG/MAX narrowbody jets. Boeing’s all-time backlog high of 5,964 aircraft was set in August 2018. The number of Airbus aircraft to be built and delivered represents 8.7 years of shipments at the 2019 production level. In comparison, Boeing’s backlog would “only” last 6.4 years at the 2018 level, which we use as a proxy for 2019 due to the severe drop in 737 MAX deliveries. This year to date, Boeing’s book-to-bill ratio, calculated as net new orders divided by deliveries, is negative due to cancellations exceeding gross orders. Airbus’ book-to-bill ratio is 1.23, mainly thanks to very strong order bookings in January. In 2019, Boeing’s book-to-bill ratio was negative, while Airbus reported a book-to-bill of 0.89.
2020 Forecast
Forecast International’s Platinum Forecast System is a breakthrough in forecasting technology that provides 15-year production forecasts. The author has used the Platinum Forecast System to retrieve the latest delivery forecasts and, for 2020, Forecast International’s analysts expect Boeing and Airbus to deliver 218 and 481 commercial jets, respectively.

Note: Boeing 777-300ER orders include one 777-200LR. The 777-300ER backlog includes two 777-200LRs.
References:
- http://www.boeing.com/commercial/#/orders-deliveries
- https://www.airbus.com/aircraft/market/orders-deliveries.html
- https://www.faa.gov/news/updates/?newsId=93206
- https://www.boeing.com/commercial/737max/737-max-update.page
- https://boeing.mediaroom.com/news-releases-statements?item=130713
- https://boeing.mediaroom.com/2020-07-29-Boeing-Reports-Second-Quarter-Results
- https://boeing.mediaroom.com/2020-04-29-Boeing-Reports-First-Quarter-Results
- https://www.bbc.com/news/business-53646442
Forecast International’s Civil Aircraft Forecast covers the rivalry between Airbus and Boeing in the large airliner sector; the emergence of new players in the regional aircraft segment looking to compete with Bombardier, Embraer, and ATR; and the shifting dynamics within the business jet market as aircraft such as the Bombardier Global 7000, Cessna Hemisphere, and Gulfstream G600 enter service. Also detailed in this service are the various market factors propelling the general aviation/utility segment as Textron Aviation, Cirrus, Diamond, Piper, and a host of others battle for sales and market share. An annual subscription includes 75 individual reports, most with a 10-year unit production forecast. Pricing begins at $2,295, with discounted full-library subscriptions available. Click here to learn more.

Based in Denmark, Joakim Kasper Oestergaard is Forecast International’s AeroWeb and PowerWeb Webmaster and European Editor. In 2008, he came up with the idea for what would eventually evolve into AeroWeb. Mr. Oestergaard is an expert in aerospace & defense market intelligence, fuel efficiency in civil aviation, defense spending and defense programs. He has an affiliation with Terma Aerostructures A/S in Denmark – a leading manufacturer of composite and metal aerostructures for the F-35 Lightning II. Mr. Oestergaard has a Master’s Degree in Finance and International Business from the Aarhus School of Business – Aarhus University in Denmark.
A military history enthusiast, Richard began at Forecast International as editor of the World Weapons Weekly newsletter. As the Internet grew in importance as a research tool, he helped design the company's Forecast Intelligence Center and currently coordinates the EMarket Alert newsletters for clients. Richard also manages social media efforts, including two new blogs: Defense & Security Monitor, covering defense systems and international issues, and Flight Plan, which focuses on commercial aviation and space systems. For over 30 years, Richard has authored the Defense & Aerospace Companies, Volume I (North America) and Volume II (International) services. The two books provide detailed data on major aerospace and defense contractors. He also edits the International Contractors service, a database that tracks all the contractors involved in the programs covered in the FI library. More recently he was appointed Manager, Information Services Group (ISG), a new unit that encompasses developing outbound content for both Forecast International and Military Periscope.



